COP26: Cleantech Startups Part 2
As COP26 nears its conclusion, we used MarktoMarket to surface a second cohort of cleantech startups aiming to pioneer the transition to net-zero.
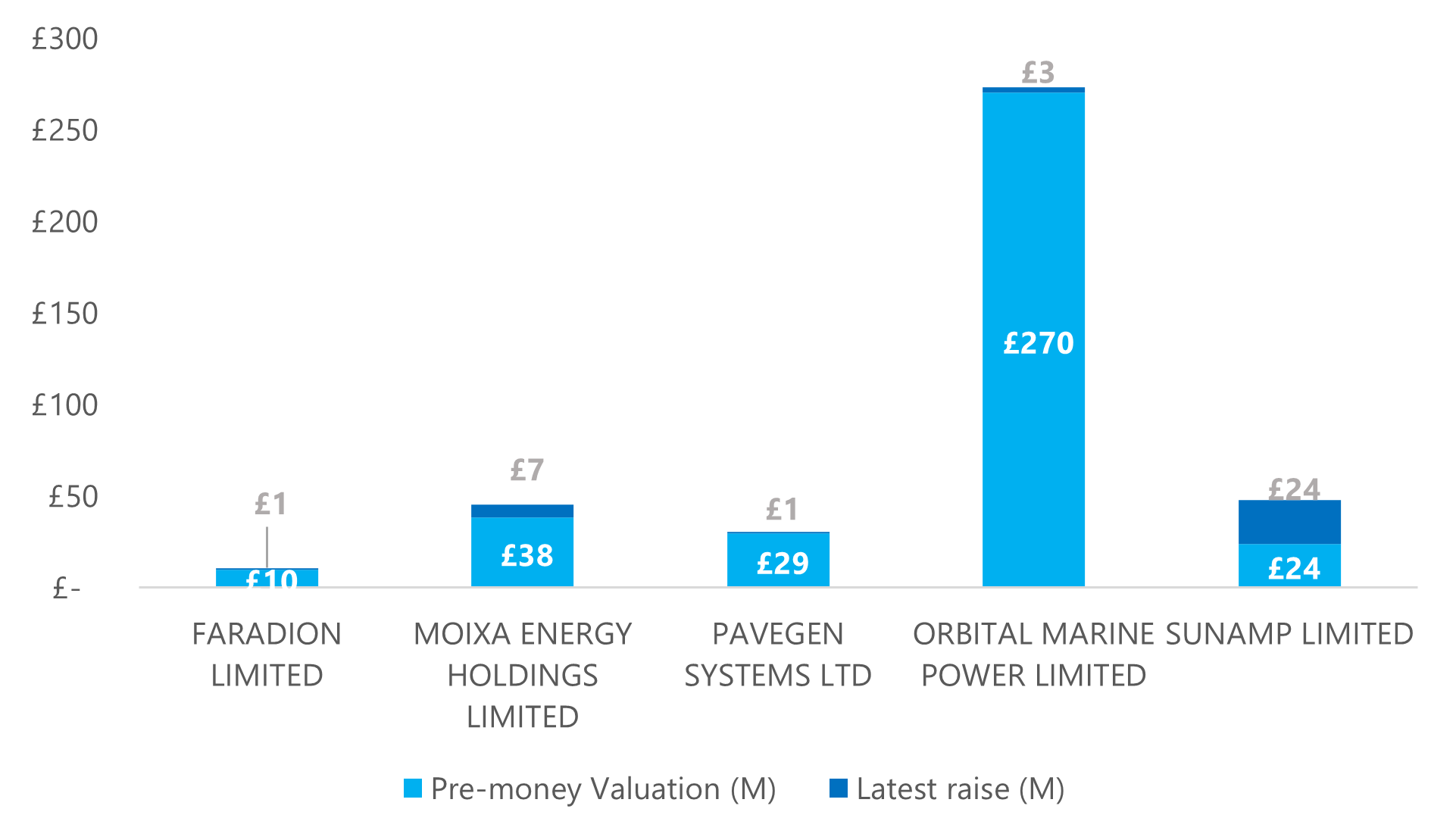
Cleantech startups: Latest round valuation and capital raise
faradion

activity – Non-aqueous sodium-ion batteries
valuation – £10.8 million
Investors – Finance Yorkshire; Mercia
Founded in 2011, Faradion is pioneering the use of sodium ions in a rechargeable battery. Faradion claims that sodium-ion is cheaper and safer than lithium-ion, with a higher energy density and a wider operating temperature range. The batteries can be used in both stationary energy storage applications and within passenger vehicles. Faradion collaborated with Williams Advanced Engineering to showcase the advantages of their batteries as a replacement for lead-acid alternatives in low-cost electric transport, namely e-scooters and e-bikes, where they can offer a far greater range and carrying capacity at a similar price. The use of sodium-ion is also being explored for starter lighter ignition in conventional batteries due to its higher energy density and improved performance over a wide temperature range.
moixa Energy

activity – Smart batteries and energy management software
valuation – £45.4 million
Investors – Itochu Corp; Honda Motor Co
Moixa’s AI-powered smart energy-management software helps renewable energy work intelligently. Named “Gridshare”, the platform facilitates and interprets interactions between energy-storage devices and the grid, enabling data-driven optimisation for local demand and consumption of renewable energy. It also allows utility companies to manage energy storage assets, based on data collected through the system. In addition to its software solution, Moixa’s smart battery is a storage device for energy generated by domestic solar panels. Instead of excess energy being sent back to the grid, to be purchased back by the household at retail prices when demand requires, it is used to recharge the Moixa smart battery, which then supplies power on demand to the home when the sun goes down. The devices have been installed in over 1,000 UK households.
Pavegen Systems

activity – Generates energy and data through footfall
valuation – £32.5 million
Investors – Renaissance Capital
Pavegen, founded by a former student at Loughborough University, has created floor tiles that convert human movement into off-grid energy. The energy generated is most frequently used for low-power lighting sources such as LEDs or monitors that can display messages around the quantum of energy being created to encourage environmentally-friendly behaviours. Its technology has been installed at running tracks, airports, schools and office buildings. At Heathow Airport, travellers walking along the Pavegen corridor trigger an interactive lighting display; at the Paris Marathon, 176 tiles were incorporated into the finishing stretch of the route along the Champs-Élysées – runners competed amongst each other on this final sprint to generate the most energy. Pavegen has turned to Crowdcube to fund the business as well as Renaissance Capital and London Business Angels.
Orbital Marine Power

activity – Tidal energy turbine technology
valuation – £294.0 million
Investors – Crowdcube; Scottish Enterprise (Renewable Energy Investment Fund)
Orbital claims to have designed the most powerful, technologically advanced tidal turbine in the world. The company is based in Orkney, which is home to some of the strongest tidal currents in the world and, therefore, a fitting environment for Orbital’s first operations. Its O2 platform and turbine is anchored in the Fall of Warness at the European Marine Energy Centre (EMEC), where it will be connected to the local electricity grid to power the communities of Orkney cleanly and sustainably. Orbital’s floating platform is moored via anchors in powerful tidal stream or river currents and its underwater rotors capture the dense flowing energy. The startup was chosen as one of only twelve companies invited to take part in the Global Investment Summit (GIS), a showcase of the most innovative cleantech companies operating in the UK.
Sunamp

activity – Thermal energy storage systems
valuation – £28.9 million
Investors – Aurus Ventures; Scottish Enterprise; Old College Capital
Over 80% of energy used in homes is for heating and hot water, and twice as much heat and cooling energy is consumed in the world economy as electricity. Sunamp’s thermal batteries use phase change materials (PCMs) to efficiently store heat for domestic hot water systems or space heating. The company’s thermal batteries contain inorganic, non-toxic, salt-based phase change materials (PCMs), which absorb and release thermal energy during the process of melting and freezing. When a PCM freezes, it releases a huge amount of energy in the form of latent heat. The batteries can be charged by electricity, air source heat pumps, ground source heat pumps, boilers and photovoltaics. The technology is being extended to industrial-scale heating/cooling applications and into the transport sector, where they are developing thermal batteries to improve engine efficiency and reduce emissions on buses.
MARKTOMARKET
MarktoMarket is a data platform and marketplace for the private capital markets.
For more details contact doug@marktomarket.io.